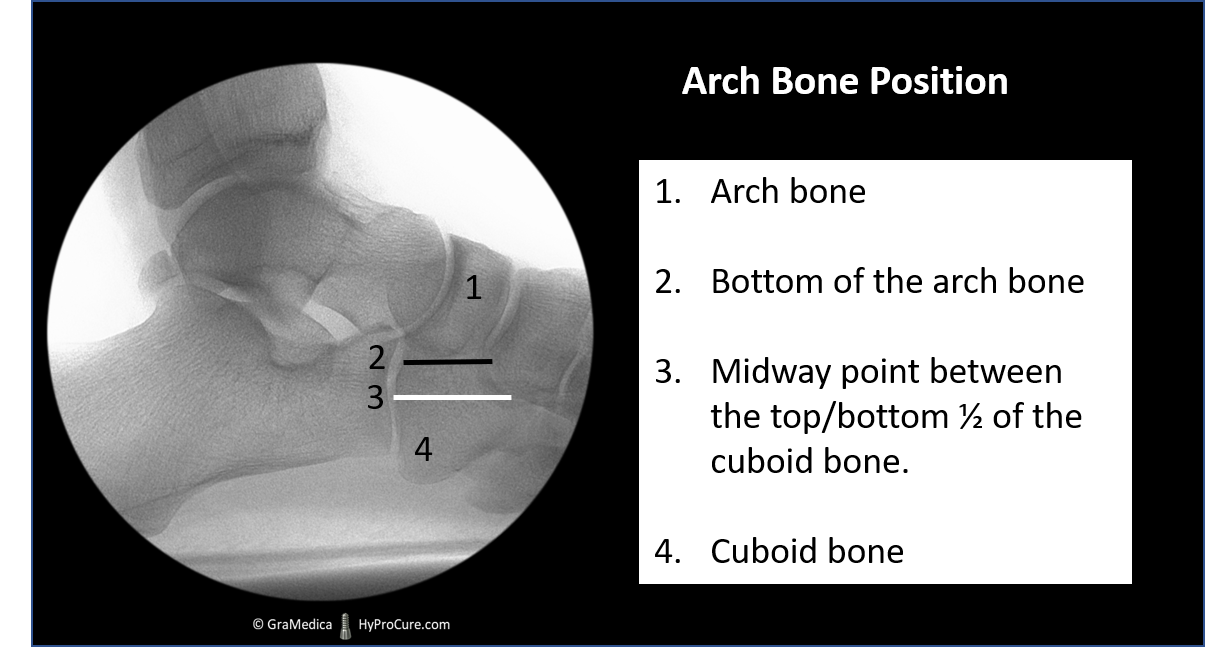
Why are fallen arches a “bad” thing?
One of the main secondary diseases related to arch bone drop is excessive strain on the posterior tibial tendon. This used to be known as “posterior tibial tendon dysfunction” and was said to be the cause of “adult acquired flat foot/feet.” The posterior tibial tendon is the major tendon that is supposed to support the inner arch. When the arch bone falls, the ligaments that attach to the arch bone are stretched. This sends a signal to the spine that in turn forces the tibialis posterior muscle to tighten. The tightening pulls the tendon that passes under the arch bone. The tendon cannot prevent the dropping of the arch bone and eventually, after more than 100 million steps, the tendon simply gets stretched out like an over-stretched rubber band.
What happens if I don’t treat my flexible falling arch?
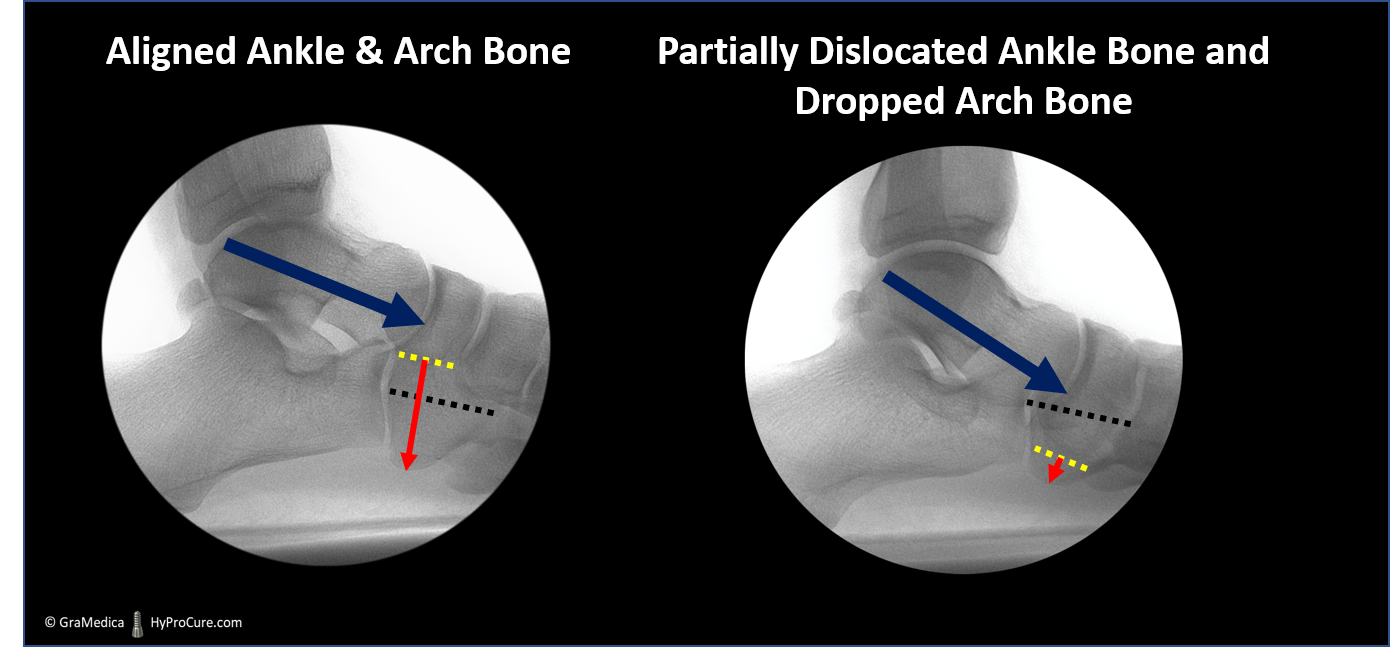
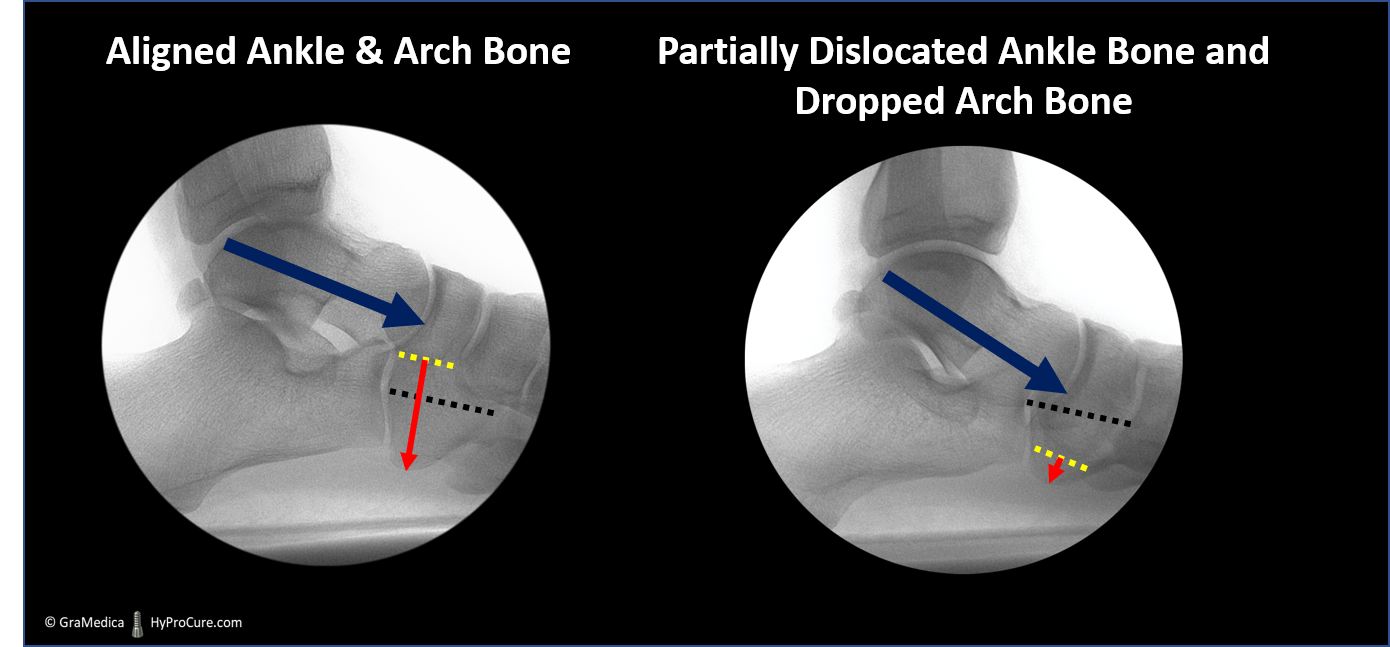
Ankle bone instability and a fallen arch bone is a dynamic deformity. The displacement and lowering of the arch only occur when there is weight on the foot when standing/walking. Eventually, it becomes a fixed deformity.
Preventative measures should be initiated with any disease process. The sooner an effective treatment is provided, the better the prognosis. A conservative option, like HyProCure, realigns the ankle bone on the heel bone. However, when the ankle bone displacement becomes fixed, when it can no longer be placed onto its normal alignment on the heel bone, then the only option is reconstructive surgery.

What’s the best form of treatment?
Unfortunately, there is not a single non-surgical option that can realign and stabilize the ankle bone. Any non-surgical form of treatment will be ineffective in preventing continued strain to the inner foot. Non-surgical forms of treatment can provide temporary relief, but the underlying disease process is still present. Every step taken is a step closer to irreversible tissue damage.
The first step to a long-term treatment plan is to identify if the ankle bone displacement is flexible or fixed. If the ankle bone can be repositioned on the heel bone, the navicular bone will be elevated. Instantly, the strain on the posterior tibial tendon is reduced/normalized. If ankle bone instability is found, the best form of treatment is the insertion of HyProCure into the sinus tarsi space. HyProCure is the only treatment proven to prevent the arch bone from dropping (DOI: 10.1053/j.jfas.2011.04.027).