Pronation is a complex motion of the foot. The ankle bone turns inward and the rest of the foot turns up and out. It’s the opposite of supination, where the ankle bone turns outward and the rest of the foot turns inward. Pronation of the foot bone is important during walking and running. It slightly unlocks the bones and joints of the foot so that the foot can adapt to an uneven ground surface.
What is over-pronation?
Over-pronation is the “common” name that means there is too-much pronation. It should really be called excessive-pronation or medically called hyperpronation, just like hypertension when someone’s blood pressure is excessive, too high. Over-pronation is not a life-threatening condition yet, it will severely affect someone’s quality of life and will eventually lead to all sorts of secondary problems to the feet, knees, hips, and back.
Why is it a “bad thing”?
Ok, big deal that the foot is in a unlocked, unstable position more than it should be, so what! Well, walking is the second most common conscious function of our body, next to breathing. Every step taken, thousands of times a day and millions of steps a year, will eventually lead to many secondary deformities. Exactly where these secondary deformities occur depends on the “weakest link of the chain.”
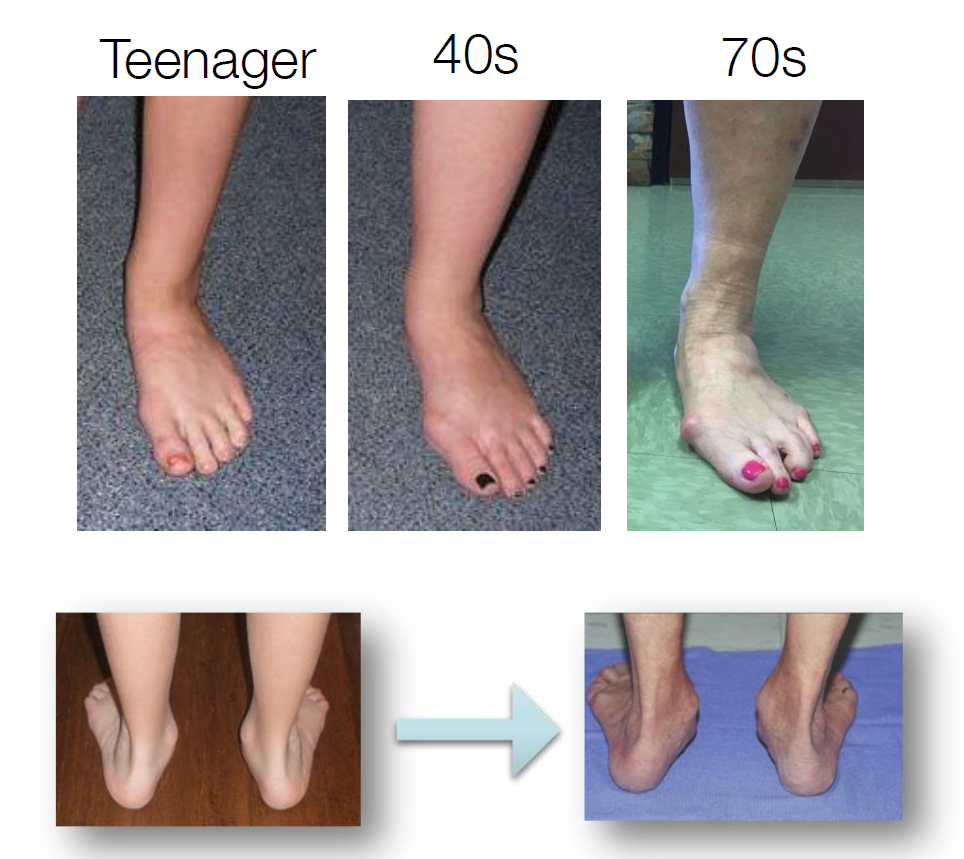
What does it do to the foot?
Over-pronation is named as the leading cause of the majority of foot problems:
Can it affect the rest of the body?
Only 20% of the symptoms show up in the foot, the rest of the symptoms show up to the rest of the body as leg, knee, hip, and back pain. The foot is the foundation to the body and a misaligned, pronating hindfoot creates an unstable foundation. The more you stand, walk, or run on a hyperpronating foot, the sooner you will experience pain to the rest of your body. It’s not if, its when!


What causes over-pronation?
Many musculoskeletal problems are caused or made worse by misaligned feet. This misalignment is the result of a common condition called talotarsal displacement. Talotarsal displacement occurs when the ankle bone slides off the heel bone. When this happens, the ankle rolls inward and causes the front of the foot to turn outward. When talotarsal displacement is left untreated, it forces the body to compensate by putting excessive strain on the heels, ankles, knees, hips and back. This causes a variety of additional symptoms, which can eventually lead to other secondary health conditions.
The solution begins with realignment and stabilization of the ankle bone.

How can HyProCure Help?
HyProCure is a small titanium stent that is inserted into the sinus tarsi fixing hyperpronation at its root by keeping the sinus tarsi in a stable open position as nature intended. This keeps your ankle bone from sliding forward and off of your heel bone and the rest of your body in its natural alignment. It is placed into a naturally-occurring space in between the ankle bone and heel bone through a small incision below the outer ankle bone. There are no pins, screws or drills required.
Unlike other stents that block your range of motion, HyProCure stabilizes the foot and restores natural joint motion. You are able to move your foot freely so that you can easily perform day-to-day activities. Since the procedure is minimally invasive, patients are typically back into their “normal” shoes within a few weeks, if not sooner.


